검색결과 리스트
분류 전체보기에 해당되는 글 192건
- 2008.11.13 데바가 되다. ^______^ (AION)
- 2008.11.12 AION.....
- 2008.11.12 하루하루의 즐거움 웹툰!!
- 2008.11.10 C Function Coding시 이렇게 하면 좋다(?)...
- 2008.11.06 Mathematics : C
- 2008.11.06 마우스 클릭 방지
- 2008.11.06 극좌표와 극방정식
- 2008.11.06 죄표계
- 2008.11.05 트랙백이란(?) For 초짜 블로거
- 2008.11.05 Linux Shell Scripting Tutorial v1.05r3 A Beginner's handbook
글
설정
트랙백
댓글
글
설정
트랙백
댓글
글
숙명이든, 운명이든....
그것이 아픔이든
고통이든 후회하며
망설이는동안 더 많은것을 잃을수도 있다
어차피 우리가 사는 이곳은
서로 죽고 죽이는 전쟁터니까
설정
트랙백
댓글
글
설정
트랙백
댓글
글
Mathematics: <math.h>
Mathematics is relatively straightforward library to use again. You must #include <math.h> and must remember to link in the math library at compilation:
cc mathprog.c -o mathprog -lm
A common source of error is in forgetting to include the <math.h> file (and yes experienced programmers make this error also). Unfortunately the C compiler does not help much. Consider:
double x; x = sqrt(63.9);
Having not seen the prototype for sqrt the compiler (by default) assumes that the function returns an int and converts the value to a double with meaningless results.
Math Functions
Below we list some common math functions. Apart from the note above they should be easy to use and we have already used some in previous examples. We give no further examples here:
double acos(double x) -- Compute arc cosine of x. double asin(double x) -- Compute arc sine of x. double atan(double x) -- Compute arc tangent of x. double atan2(double y, double x) -- Compute arc tangent of y/x, using the signs of both arguments to determine the quadrant of the return value. double ceil(double x) -- Get smallest integral value that exceeds x. double cos(double x) -- Compute cosine of angle in radians. double cosh(double x) -- Compute the hyperbolic cosine of x. div_t div(int number, int denom) -- Divide one integer by another. double exp(double x -- Compute exponential of x double fabs (double x ) -- Compute absolute value of x. double floor(double x) -- Get largest integral value less than x. double fmod(double x, double y) -- Divide x by y with integral quotient and return remainder. double frexp(double x, int *expptr) -- Breaks down x into mantissa and exponent of no. labs(long n) -- Find absolute value of long integer n. double ldexp(double x, int exp) -- Reconstructs x out of mantissa and exponent of two. ldiv_t ldiv(long number, long denom) -- Divide one long integer by another. double log(double x) -- Compute log(x). double log10 (double x ) -- Compute log to the base 10 of x. double modf(double x, double *intptr) -- Breaks x into fractional and integer parts. double pow (double x, double y) -- Compute x raised to the power y. double sin(double x) -- Compute sine of angle in radians. double sinh(double x) - Compute the hyperbolic sine of x. double sqrt(double x) -- Compute the square root of x. void srand(unsigned seed) -- Set a new seed for the random number generator (rand). double tan(double x) -- Compute tangent of angle in radians. double tanh(double x) -- Compute the hyperbolic tangent of x.
Math Constants
The math.h library defines many (often neglected) constants. It is always advisable to use these definitions:
- HUGE -- The maximum value of a single-precision floating-point number.
- M_E -- The base of natural logarithms (e).
- M_LOG2E -- The base-2 logarithm of e.
- M_LOG10E - The base-10 logarithm of e.
- M_LN2 -- The natural logarithm of 2.
- M_LN10 -- The natural logarithm of 10.
- M_PI --
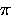 .
.
- M_PI_2 --
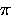 /2.
/2.
- M_PI_4 --
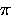 /4.
/4. - M_1_PI -- 1/
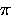 .
.
- M_2_PI -- 2/
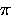 .
.
- M_2_SQRTPI -- 2/
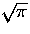 .
.
- M_SQRT2 -- The positive square root of 2.
- M_SQRT1_2 -- The positive square root of 1/2.
- MAXFLOAT -- The maximum value of a non-infinite single- precision floating point number.
- HUGE_VAL -- positive infinity.
There are also a number a machine dependent values defined in #include <value.h> -- see man value or list value.h for further details.
설정
트랙백
댓글
글
설정
트랙백
댓글
글
설정
트랙백
댓글
글
1. 개요
| 공간상의 한 물체 또는 한점의 위치는 일반적으로 좌표로써 표시된다. 위치란 어느 좌표계에 있어서 다른 점들과 어떤 기하학적인 상관관계를 갖는가를 의미하는 것으로, 일반적으로 그 좌표계의 특정점 또는 특정선으로부터의 길이와 방향을 매개로 하여 표현한다. 이때 어느 좌표계의 기준이 되는 고유한 한 점을 원점(origin), 매개가 되는 실수(어떤 길이, 또는 방향 등)을 좌표(Coordinate)라 한다. |
2. 좌표계의 종류
1) 1차원 좌표계
1차원좌표는 주로 직선과 같은 1차원선형에 있어서 점의 위치를 표시하는데 쓰인다. 예를 들면, 직선상에 등속운동하는 물체를 생각할 때 어느 시점에서 이 물체의 위치는 기준점으로부터의 거리로 표시되며 이것은 시간과 속도의 함소로 나타냇 수 있을 것이다. |
<1차원좌표>

2) 2차원 좌표계
a. Cartesian Coordinate
평면상의 1점의 위치를 표시하는데 있서 가장 대표적인 좌표계이다. 평면위에 한 점 O를 원점으로 정하고, O를 지나고 서로 직교하는 두 수직직선 XX´, YY´를 좌표축으로 삼는다. 평면상의 한 점 P위의 위치는 P를 지나며 X, Y축에 평행한 뒤 직선이 X, Y축과 만나는 P´ 및 P˝의 좌표축상 선분OP´ = x, 선분 OP˝ = y로 나타낼 수 있다. 측 평면상 한점 P의 위치는 두 개의 실수의 순서쌍(x, y)에 대응하며, 역으로 순서쌍(x,y)가 주어지면 두 좌표축으로부터 P의 위치가 결정된다. |
<평면직교좌표>

b.Plane Oblique Coordinate
| 평면상 1점의 위치를 표시하기 위해서 임의의 각도로 경사되어 교차하는 두개의 수치직선을 좌표축으로 도입한 것으로 윗 그림의 오른쪽과 같이 평면상에서 교차하는 두 개의 수직직선을 각각 X, Y좌표축으로 잡고 그 교점 O를 원점으로 한다. |
<평면사교좌표>

c.Plane Polar Coordinate
| 2차원극 좌표는 평면상 한점과 원점을 연결한 선분의 길이와 원점을 지나는 기준선과 그 선분이 이루는 각으로 표현되는 좌표이다. 극각 θ는 수학적 좌표계에서는 반시계방향으로 +로 하지만, 일반측량에서는 방위각 등과 같이 통상 시계방향을 +로 한다. |
| θ : Polar angle O : pole OX : Initial line or Polar axis Cartesian Coordinate(x,y)와 Plane Polar Coordinate(r, θ)의 관계는 다음과 같다. r=Γx² + y², θ=tan-¹(y/x) x = r cos θ, y =r sinθ |
<Plane Polar Coordinate>

a. Three-Dimensional Cartesian Coordinate
3차원 직교좌표는 공간의 위치를 나타내는데 가장 기본적으로 사용되는 좌표계로서 평면직교좌표계를 확장한 것으로, 서로 직교하는 세 축 OX, OY, OZ로 이루어진다. 공간에서 P(x,,y,z)의 3차원 직교좌표는 P를 지나며 각 축에 대해 수직을 이루는 평면들이 지나는 좌표축으로부터 읽을 수 있다. |
| OP의 길이 ρ는 세 좌표로 부터 다음 식으로 계산된다. ρ = Γx²+y²+ z² 또 OP가 X, Y, Z축과 이루는 각을 α,β,γ 일때 cos²α + cos²β + cos²γ = x²/ρ² + y²/ρ² + z²/ρ² =1 |
<Three-Dimensional Cartesian Coordinate>

c.Three-Dimensional Oblique Coordinate)
| 공간에 한 점 O를 원점으로 정하고, O를 지나며 서로 직교하지 않는 세 평면상에 O를 지나는 세 개의 수치직선 XOX´, YOY´, ZOZ´를 좌표축으로 잡는다. OX, OY, OZ를 양의 반직선으로 하는 좌표계를 도입하면 공간상 한 점 P에 대하여 세 개의 실수의 순서쌍이 대응된다. 즉 점 P를 지나며 세 걔의 기준평면 YOZ, XOZ, XOY에 평행한 세 평면이 세 좌표축 XX´,YY´,ZZ´과 만나서 점을 각각 L, M, N이라 하면 각 좌표축상의 길이는 선분OL =x , 선분 OM=y, 선분ON=z로써 점 위치를 좌표(x,y,z)로 지정할 수 있다. |
<Three-Dimensional Oblique Coordinate>

c.Cylindrical Coordinate
| 공간에서 점의 위치를 표시하는데 원주좌표가 종종 편리하게 쓰이고 있으며, 평면 z=0 위의 (x,y) 대신 극좌표(Υ,θ)를 사용한다. 공간에서 O점을 원점으로 하는 직교좌표를 잡고 공간의 점 P(x,y,z)에서 X,Y 평면엣 수선 PP´를 내려서 OP´ = Υ, ∠XOP = θ , PP = z라 하여 P점을 (Υ,θ,z )로 표현한다. |
<Cylindrical Coordinate>

c.Spherical Coordinate
| 이 좌표계에서는 어떤 점의 위치를 하나의 길이와 두개의 각으로 나타낸다. 원점을 중심으로 대칭일 때 유용하다. 공간에서 O점을 직교좌 표축을 잡고 공간의 점 P(x,y,z)에 대하여 OP = ρ ∠ZOP = φ라고 하고, XY평면에 수선 PP´를 내려서 ∠XOP´ = θ라 하여 점 P를 (ρ, θ, φ)로 표현한다. |
<Spherical Coordinate>

4) 지구좌표계
a. Geographic Coordinate
| 지구상 절대적 위치를 표시하는데 일반적으로 가장 널리 쓰이는 좌표계이다. 3차원구면 좌표계에서 구의 반경 ρ와 두개의 편각 θ,Φ로 구성되는 세 개의 실수(ρ,θ,Φ)가 대응하여야 하지만 통상 지구좌표계에서는 경도 λ와 위도 φ에 의한 좌표(λ,φ)로 수평위치를 나타낸다. 따라서 3차원 위치를 표시하려면 타원체면으로부터 높이, 또는 표고를 도입할 필요가 있다. 지구 타원체를 동서방향의 위도선과 남북방향의경도선을 도, 분, 초로 표시하며 투영법의 종류에 관계없이 임의의 위치점을 표현할 수 있다. 적도선을 0도 기준으로 하여 남북으로 각각 90도씩 적도에 평행하게 그은 선을 위도선이라 하며 적도를 중심으로 북쪽으로는 북위, 남쪽으로는 남위라고 한다. 또한 경도선은 일명 자오선이라고도 하는데 영국의 그리니치 천문대를 통과하는 본초자오선을 0도 기준으로 하여 동쪽으로 180도까지를 180등분한 선을 동경이라고 한다. 위도는 어느 지점의 연직선(또는 타원체의 법선)이 적도면과 이루는 각으로 정의할 수 있는데, 연직선과 타원체의 법선은 통산 일치하지 않고, 또 정희하는 방법에 따라 측지위도, 천문위도, 지심위도, 화성위도 등으로 구분한다. |
< 경위도좌표>

< 위도별 경도의 길이 >
위도 (° ) |
위도 1도의 길이(km) |
경도 1도의 길이 (km) |
0 |
110.569 |
111.322 |
b. TM(Transverse Mercator)
| TM 좌표는 임의의 지역에 대한 기준 지점을 좌표 원점으로 정하고 원점을 중심으로 TM투영한 평면상에서 원점을 지나는 자오선을 X축, 동서방향의 위도선을 Y축으로 하여 각 지점의 위치를 m단위의 평면 직각좌표계로 표시한다. 이것은 수학에서의 좌표축과는 다르다 우리나라에서는 TM 좌표 또는 평면 직각좌표계에서의 좌표 기준점으로 서부 원점(125° E, 38° N), 중부 원점(127° E, 38° N), 동부 원점(129° E, 38° N)의 3개 원점을 사용한다. 여기서 X축은 북쪽 방향이 양의 값을 나타내고, Y축은 동쪽 방향이 양의 값을 나타난다. 우리나라의 평면직각좌표의 원점은 통일원점 3개, 기타원점 11개로 구성되어 있다. 통일원점은 북위 38도, 동경 125도, 127도, 129도로 3개원점이 위치하고 있고, 각각의 평면직교좌표계에서 모든 지역의 좌표가 양수가 되게 하기 위해 종축(X축)에는 500,000m(단, 제주도는 550,000m), 횡축(Y축)에는 200,000m를 더합니다. 기타원점은 구소삼각측량 시행지역에 위치하는 것으로 경기도 지역과 경북지역에 있으며 그 현황은 다음과 같다 |
< 우리나라 원점계 >
| 구분 | 원점명 | 경도 | 위도 |
| 통일원점 | 서부 중부 동부 |
125° 127° 129° |
38° 38° 38° |
| 기타원점 | 망 산 계 양 조 본 가 리 동 경 고 초 율 곡 현 창 구 암 금 산 소 라 |
126° 22´ 24.596˝ 126° 42´ 49.658˝ 127° 14´ 07.397˝ 126° 51´ 59.430˝ 126° 51´ 32.845˝ 127° 14´ 41.585˝ 128° 57´ 10.915˝ 128° 46´ 03.947˝ 128° 35´ 46.186˝ 128° 17´ 26.070˝ 128° 43´ 36.841˝ |
37° 43´ 07.060˝ 37 ° 33´ 01.126˝ 37° 26´ 35.262˝ 37° 25´ 30.532˝ 37° 11´ 52.885˝ 37° 09´ 30.530˝ 35° 57´ 21.322˝ 35° 51´ 46.967˝ 35° 51´ 30.878˝ 35° 43´ 46.532˝ 35° 39´ 58.199˝ |
c. UTM(Universal Transverse Mercator)
| UTM 투영법에 의하여 표현되는 좌표계로서 적도를 횡측, 자오선을 종축으로 한다. 이 방법은 지구를 회전타원체로 보고 지구전체를 경도 6°씩 60개 구역(종대, column)으로 나누고 그 각 종대의 중앙자오선과 적도의 교점을 원점으로 하여 원통도법인 횡 Mercator(TM) 투영법으로 등각투영한다. 각 종대는 180°W 자오선에서 동쪽으로 6°간격으로 1부터 60까지 번호를 붙인다. 종대에서 위도는 남. 북에 80까지만 포함시키며 8°간격으로 20구역(row)으로 나누어 C(80°S ~ 72°S)에서 X(72°N ~ 80°N)까지 (단, I와 O는 제외) 알파벳 문자로 표시한다. 따라서 종대 및 횡대는 결국 경도 6° X 8°의 직각형 구역으로 구분된다. UTM좌표에서 거리좌표는 m 단위로 표시하며 종좌표에서는 N을, 횡좌표에서는 E를 붙인다. 각 종대마다 좌표원점의 값을 북반구에서 횡좌표 500,000mE, 종좌표 0mN(남반구에서는 10,00,000N)으로 주면 북반구에서 종좌표는 적도에서 0mN, 80°N에서 10,000,000mN이고, 남반구에서는 80°S에서 적도까지의 거리는 10,000,000m로 나타난다. 80°N과 80°S간 전 지역의 지도는 UTM좌표로 표시하며 80°N이북과 80°S이남의 양극지역의 전 지역의 지도는 국제극심입체좌표(UPS)로 표시함으로써 전 세계를 일관된 좌표계로 나타낼 수 있다. 지도 1장의 도곽을 구성하는 경위선을 서로 직교하는 곡선으로 나타나며 1/50,000 이상에서는 실용상 직선으로 보아도 무방하다. Gauss-Kruger 투영에서는 중앙경선의 길이가 지구상과 같지만(선확대율 Kο =1) UTM투영에서는 Kο=0.9996으로 축호한 지역의 오차는 ±4/10,000 ~ 6/10,000정도이다. 처음 UTM좌표는 세계 제2차세계대전 말기 연합군의 군용거리좌표로 고안된 것으로 주로 군용좌표로 사용되어 왔으나 지도제작과 사용상 편리함 점이 많으므로 근래에는 세계적으로 대축척 지도좌표로 널리 사용되어 왔다. 우리나라의 경우 UTM좌표 구역은 그림 II-9에서와 같이 동서 방향으로 51, 52구역 및 남북방향으로, S, T 구역에 속한다. 51구역의 경우 중앙 자오선은 123° E 이며 52구역은 129° E가 된다. 또한 32° N에서 40° N 구역은 S로 표기하며 40° N에서 48° N 까지는T구역으로 표시한다. UTM 좌표를 표기하는 예로 경위도좌표 37° 43’ 36’N, 127° 13’ 55’E 의 경우WGS84 타원체기준으로 UTM좌표로 표기하면 52 S 구역의 (4,176,960mN , 344,189mE)로 나타낼 수 있다. |
< 그림 UTM 좌표 >

d. UPS(Universal Polar Stereographic)
| UPS좌표는 위도 80°이상의 양극 지역의 좌표를 표시하는데 사용한다. 이 좌표계는 양극을 원점으로 하는 평면직교좌표계를 사용하며, 거리좌표는 m단위로 나타낸다. 좌표의 종축은 경도 0° 및 180°인 자오선이고 횡축은 90° W및 90° E인 자오선이다. 원점의 좌표값은 횡좌표 2,000.000mE, 종좌표 2,000,000mN이며 도북은 북극을 지나는 180° 자오선(남극에서는 0° 자오선)과 일치한다. 가로선의 끝좌표는 북극의 경우 경도 0도 부근의 최하단 횡선이 1,000,000mN, 원점이 2,000,000mN, 경도 180° 부근의 최단 횡선이 3,000,000mN이다. 세로선은 90° W부근이 1,000,000Mn, 원점이 2,000,000mN, 90° E부근이 3,000,000mN이다. 남극의 경우는 경향이 반대에 해당된다. 북극 지역은 84° N까지를 UPS좌표로 표현할 수 있으며 남극 지역은 80° 까지 표현할 수 있다. |
<UPS좌표방안>
설정
트랙백
댓글
글
트랙백 (Trackback)은 블로그에서 사용하는 주요기능 중 한가지로, 간단히 역방향 링크를 자동적으로 생성해 준다. 블로그 이외에 위키위키나 뉴스 사이트에서 제공하기도 한다.
트랙백은 철저한 1인 미디어를 지향하는 블로그들 사이의 연결고리를 만들어 주어 소통 네트워크를 만들어 내는 역할을 한다. 누군가의 블로그를 읽고 그에 대한 의견을 자신의 블로그에 써 넣은 후 트랙백을 주고 받으면 원래 글 아래 새로운 글로의 링크가 붙게 된다.
표준,
트랙백 표준은 2002년 Movable Type 블로깅 소프트웨어를 개발한 Six Apart에 의해 작성되었다. 그 후 대부분의 다른 블로깅 도구들도 이를 구현해왔다. Six Apart은 2006년 2월에 트랙백 프로토콜을 향상시키기 위해 워킹 그룹을 출범하였으며, IETF는 이를 표준으로 등록하였다.
단점,
일부 개인이나 회사들은 트랙백을 사용하여 스팸 링크를 넣을 수 있는 특성에 대해 지적해왔다. 댓글 스팸과는 달리 트랙백 스팸 필터의 개발이 상대적으로 늦었다. 현재의 블로그 도구들은 트랙백 스팸도 처리할 수 있지만 일부 블로거들은 트랙백 스팸 때문에 트랙백을 끄기도 한다.
설정
트랙백
댓글
글
Linux Shell Scripting Tutorial v1.05r3 |
Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: Quick Introduction to Linux
- What Linux is?
Who developed the Linux?
How to get Linux?
How to Install Linux
Where I can use Linux?
What Kernel Is?
What is Linux Shell?
How to use Shell
What is Shell Script ?
Why to Write Shell Script ?
More on Shell... - Chapter 2: Getting started with Shell Programming
- How to write shell script
Variables in shell
How to define User defined variables (UDV)
Rules for Naming variable name (Both UDV and System Variable)
How to print or access value of UDV (User defined variables)
echo Command
Shell Arithmetic
More about Quotes
Exit Status
The read Statement
Wild cards (Filename Shorthand or meta Characters)
More commands on one command line
Command Line Processing
Why Command Line arguments required
Redirection of Standard output/input i.e. Input - Output redirection
Pipes
Filter
What is Processes
Why Process required
Linux Command(s) Related with Process - Chapter 3: Shells (bash) structured Language Constructs
- Decision making in shell script ( i.e. if command)
test command or [ expr ]
if...else...fi
Nested ifs
Multilevel if-then-else
Loops in Shell Scripts
for loop
Nested for loop
while loop
The case Statement
How to de-bug the shell script? - Chapter 4: Advanced Shell Scripting Commands
- /dev/null - to send unwanted output of program
Local and Global Shell variable (export command)
Conditional execution i.e. && and ||
I/O Redirection and file descriptors
Functions
User Interface and dialog utility-Part I
User Interface and dialog utility-Part II
Message Box (msgbox) using dialog utility
Confirmation Box (yesno box) using dialog utility
Input (inputbox) using dialog utility
User Interface using dialog Utility - Putting it all together
trap command
The shift Command
getopts command - Chapter 5: Essential Utilities for Power User
- Preparing for Quick Tour of essential utilities
Selecting portion of a file using cut utility
Putting lines together using paste utility
The join utility
Translating range of characters using tr utility
Data manipulation using awk utility
sed utility - Editing file without using editor
Removing duplicate lines from text database file using uniq utility
Finding matching pattern using grep utility - Chapter 6: Learning expressions with ex
- Getting started with ex
Printing text on-screen
Deleting lines
Coping lines
Searching the words
Find and Replace (Substituting regular expression)
Replacing word with confirmation from user
Finding words
Using range of characters in regular expressions
Using & as Special replacement character
Converting lowercase character to uppercase - Chapter 7: awk Revisited
- Getting Starting with awk
Predefined variables of awk
Doing arithmetic with awk
User Defined variables in awk
Use of printf statement
Use of Format Specification Code
if condition in awk
Loops in awk
Real life examples in awk
awk miscellaneous
sed - Quick Introduction
Redirecting the output of sed command
How to write sed scripts?
More examples of sed - Chapter 8: Examples of Shell Scripts
- Logic Development:
Shell script to print given numbers sum of all digit
Shell script to print contains of file from given line number to next given number of lines
Shell script to say Good morning/Afternoon/Evening as you log in to system
Shell script to find whether entered year is Leap or not
Sort the given five number in ascending order (use of array)
Command line (args) handling:
Adding 2 nos. suppiled as command line args
Calculating average of given numbers on command line args
Finding out biggest number from given three nos suppiled as command line args
Shell script to implement getopts statement.
Basic math Calculator (case statement)
Loops using while & for loop:
Print nos. as 5,4,3,2,1 using while loop
Printing the patterns using for loop.
Arithmetic in shell scripting:
Performing real number calculation in shell script
Converting decimal number to hexadecimal number
Calculating factorial of given number
File handling:
Shell script to determine whether given file exist or not.
Screen handling/echo command with escape sequence code:
Shell script to print "Hello World" message, in Bold, Blink effect, and in different colors like red, brown etc.
Background process implementation:
Digital clock using shell script
User interface and Functions in shell script:
Shell script to implements menu based system.
System Administration:
Getting more information about your working environment through shell script
Shell script to gathered useful system information such as CPU, disks, Ram and your environment etc.
Shell script to add DNS Entery to BIND Database with default Nameservers, Mail Servers (MX) and host
Integrating awk script with shell script:
Script to convert file names from UPPERCASE to lowercase file names or vice versa. - Chapter 9: Other Resources
- Appendix - A : Linux File Server Tutorial (LFST) version b0.1 Rev. 2
Appendix - B : Linux Command Reference (LCR)
About the author
About this Document


RECENT COMMENT